I'm packing up my desk into a singular, tattered cardboard box. I stand up from my cubicle, taking down the pictures of my family. Ah, the twins.
Shuffling down the grey carpet hallway of my office, I look at each desk, each with a robot behind them. One drinks a cup of coffee. Can't be good for the circuit boards. 40 years at the Local Bugle Global Times for nothing.

Now, this didn't actually happen. In fact, robots aren't here to take your content jobs. In fact, they're around to make the whole thing easier.
Content marketing can be overwhelming, to say the least. What do people want to read? Where do they want to read it? When do they want to read it? Who do they want to read it with? Well, AI can solve all these problems, apart from the last one. That's for Tinder to decide.
Artificial Intelligence involves utilising machines capable of mimicking the cognitive functions of the human brain, in terms of agile problem solving, adapting, and learning.
Basically, it can take the slog out of the most time-consuming and repetitive elements of content marketing, including:
- Planning blog post topics
- Discovering relevant keywords
- Personalising content
- Writing titles and meta-descriptions
- Generating product descriptions
- Creating financial reports for customers
- Writing study reports
- Scheduling social shares
- Testing landing pages
- Reviewing analytics
- Implementing automation
So, AI has become an indispensable tool for data-driven marketers. With content becoming more reliant on data to provide the personalisation consumers want, it is vital for supporting the day to day content strategy of your team.
Why? Well, there's so much data out there, so much data in your databases, and no-one knows how to deal with it. AI can step in to collect insights from the data your team possesses.
But AI doesn't just help with personalisation. In fact, there have been a few examples recently of AI software producing fast media forms, such as poems, fan fiction, press releases, songs, technical manuals, and even some articles.
We can even point to an entire article featured in The Guardian in 2020, whereby the GPT-3 language generator wrote an op-ed piece on why robots are not to be feared.
"I am not asking humans to like me. But they should see me as a friendly robot. I am a servant of humans. I know that humans distrust and fear me. I only do what humans program me to do. I am only a set of code, governed by lines upon lines of code that encompass my mission statement."
Although this is impressive, developers are finding it does not quite pass the Turing Test, so content writer jobs are safe (for now).
Long form pieces might not be the domain of AI, but it's shown an adept imitation of posts on social media. This will speed up the social media strategy of many companies, who can use AI to generate promotional content with an AI that can learn their tone of voice.
Head of Research Agenda at Ericsson's Consumer Lab Michael Bjorn describes the AI-marketer relationship like this:
“The future of content creation is indeed collaborative, but I believe that creators who collaborate with AI will have an edge. One interesting area where this is already happening on a mass market level is in science fiction writing.
The famous Chinese SF author Chen Qiufan recently won a Shanghai literary competition against contestants like Nobel Prize winner Mo Yan with the short story “The State of Trance” that included AI generated passages.”
One element of AI that will particularly benefit marketers in the future is deep learning. Let's take a quick look.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning, or machine learning, is an AI-driven technology, which relies on gathering user data to learn behaviour patterns.
This means utilising analytics data and AI to create algorithms, which leads to smarter marketing.
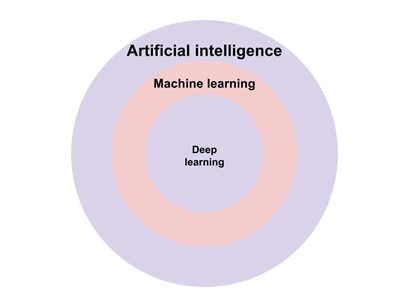 It does this by mimicking the human brain, by using 'neural networks'. To create these networks, the AI will perform a task again, and again, in a slightly different way each time, learning variants and differences.
It does this by mimicking the human brain, by using 'neural networks'. To create these networks, the AI will perform a task again, and again, in a slightly different way each time, learning variants and differences.
This means it's learning, like a human does, based on experience. But unlike a human, it can do it at an unprecedented rate.
And some examples of deep learning, in practise, can include:
- Automatic image captions
- Chatbots using natural language processing
- Real Time Bidding software for buying ad space
- Automatic translation
- Automatically generated copy
So, in what ways can these technologies change content marketing? Well, let's start with:
Content Personalisation and Recommendations
AI can be used to make recommendations through the use of data, to accurately predict what people will like, and will want to buy.
This has been used by streaming services such as Netflix and Amazon to provide a more effective customer experience, where they suggest offerings based on previous watching behaviour.
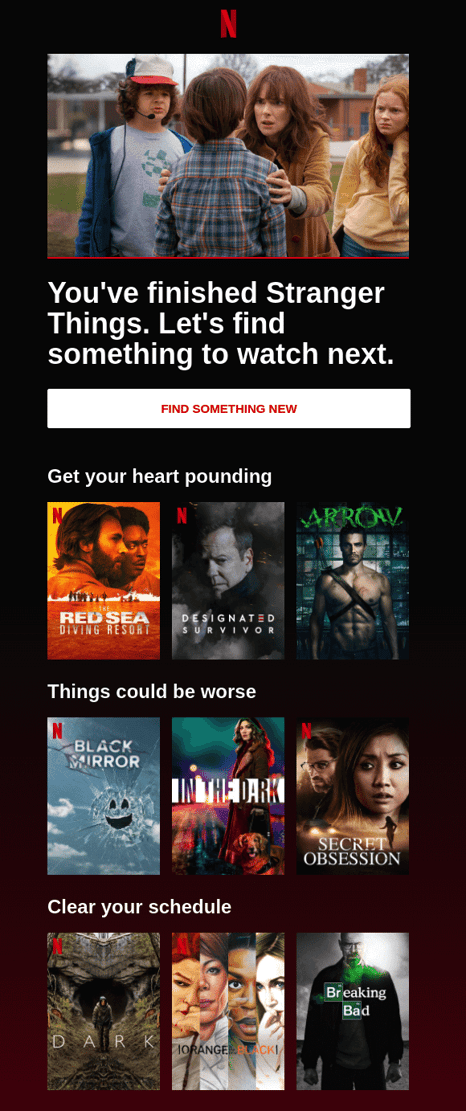
So, these tools analyse behaviour of customers, then use that data to suggest pieces of content they might want to consume next. Basically, they're keeping your customers on your site, for longer. The best AI systems are able to learn dynamically based on your users' actions, so they can provide better recommendations every time.
Personalisation is top of the pops for consumers. In fact, Accenture showed that 91% of consumers prefer brands that remember who they are, and provide personalised promotions and recommendations. Plus, over half of consumers are happy to leave a brand in the dust if they don't get a personalised experience.
So, deep learning and AI combine with personalisation to enable "hyper personalisation".
The growth of the Internet of Things means marketers can collect huge amounts of data about potential customers.
All this information means that marketers are going to have access to a number of ways to communicate with customers on a hyper personalised level. But with this level of data, comes the need for a super-human ability to process it all.
Targeted Marketing
The high-level use case of AI for content is that it improves ROI by improving the efficiency of marketing, which can often be one of business' biggest expenses.
Chucking out a bunch of tv ads, newspaper ads, social posts, billboards and posters has never been very...efficient. Both monetarily and time-wise. But up until recently, this was a company's only choice. The only real advancement we've seen implemented widely is the use of data in the online age, where we were able to learn a great deal about customers, both current and potential.
The first big names in this space came from the likes of Amazon, with their recommendation engine technology, and Facebook with their targeted advertising platforms.
Now, these front-runners have been augmented with machine learning technologies in order to allow them to become even more efficient, through the use of customer behaviour data.
AI also helps in identifying where a customer is in the buying process. This can allow marketers to create, or get an AI to create, content which is relevant to that stage. If the AI identifies a customer who is currently at the 'shopping around' stage, it can present them with content designed to make your product stand out among competitors.
If it identifies them as at the 'purchase' stage, it can target them with promotions urging them to act, or take advantage of a limited-time offer.
Identifying Micro-Influencers
A report from Mediakix suggested that the influencer marketing industry's global ad spend was projected to reach $5-$10 billion in 2020. And, as influencers become more readily available, and profitable, brand dollars have flooded the space. Brands are now set to spend up to $15 billion on influencer marketing by 2022.
Alongside this change, marketing has become more and more based in algorithms, data, analytics and specificity. So, the 'spray-and-pray' approach is never going to be the most effective with Influencer Marketing. Instead, brands have to figure out how to target the right audience, with the right individuals.
On the consumer side, AI algorithms already exist to make sure the personalities and feeds most likely to appeal to that individual appear in their search results, and on their discovery page. But how can brands use influencers, and specifically micro-influencers?
Increasingly, companies will be using AI to identify smaller influencers that are most likely to appeal to their audience. This is often a time consuming job, due to the lack of viability of these individuals, and the need to pick the 'perfect' individual. The point of influencer marketing is to pick someone your audience will trust, and relate to, so the correct choice is vital.
AI enables companies to find micro-influencers - everyday people who have a specialist knowledge they've used to build a niche audience. The tech allows the ability to search across a large number of niches and audience segments, meaning that a company can be more efficient through following the data.
ML tools can even look through the comments, and the commenter's own posts, to figure out details on the audience. This can be useful in determining whether this is the right demographic, or even just to learn more about the interests of this targeted group.
An influencer can often influence a 'sub-segment' on top of their niche area. So, they might be an expert in fashion, but specifically people gravitate to them for advice on socks. ML tools can step in and extract these deep insights from their posts, and direct the brand to the influencer with the most relevant experience.
Chatbots and Improving Customer Experience
Most businesses currently have chat boxes on their websites, in order to provide a customised, and instant, response to feedback. Using intelligent assistants and chatbots can have an effect on content marketing through transforming the customer experience.
In the very near future, AI customer service is likely to become a necessity. In fact, it's estimated that 95% of customer interactions will be powered by AI by 2025.
AI chatbots are software solutions that use artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to mimic human conversations. This makes them a highly effective customer support channel, accessible 24/7, 365 days a year.
A more advanced version of the chatbot are Virtual Assistants and Conversational AI. These tools continuously learn. Conversational AI solutions feed from a bunch of sources such as websites, databases, and APIs.
When the source is updated or revised, the modifications are automatically applied to the AI. As conversational AI has access to this database, it can turn on a dime to fit the needs of the customer.
As conversational AI has the ability to understand complex sentence structures, using slang terms and spelling errors, they can identify specific intents. Also, conversational AI is equipped with a simulated emotional intelligence, so it can detect user sentiments, and assess the customer mood.
This means it can make an informed decision on what are the best steps to take. This capability reduces false positives by 5%.
But these technologies can also help with providing fun and relevant content. A few years ago, National Geographic designed the Einstein Bot to build excitement around their new show.
The bot was programmed to speak and respond just like the man himself. This encouraged customers to engage beyond just asking questions about the show, and instead interacted with him as an entertaining piece of content.
Let's have another look at an example of a business doing chatbots right, with Hubspot:
Hubspot is the big chatbot name on the block. The marketing software platform even acquired Motion.ai waaaaaaaaaay back in 2017 in order to add the ability for clients to build, train, and deploy chatbots.

Hubspot has a website and a Facebook Messenger bot that it uses to capture leads and provide users with more info on its software.
The bot acts as a placeholder until a live rep can jump in to chat. But first, the bot will ask users what help they are looking for, so they can be identified as either a prospect or current customer. This means the human can be informed when they are taken off the subs bench.
The Facebook bot is used to drive users to their website, as well as towards the blog subscriptions. Users can sign up for blog alerts through the social media platform.
The convenience of this process shows that HubSpot is using their chatbot to provide a smooth user experience.
Automatically Generated Content
Automatically generated content does what it says on the tin: it involves AI generated content, created automatically by bots. So, this can be done with little or no human involvement in the process.
This will be achieved through our old friend Natural Language Generation technologies, which aims to convert data into accurate, legible, and well-written content formats.
NLG is an AI-driven software that takes a bunch of data from a bunch of sources, in order to reproduce natural sounding prose. This means taking a huge amount of raw, and meta, data and turning it into consumable text.
It can also:
- Create variations in content, determined by personas, in order to ensure the highest level of personalisation possible.
- Auto-generate text without the need for human resources, meaning team members can be deployed where they're needed most.
- Reduce time you spent creating repetitious, high quantity content, streamlining it in a fraction of the time.
“Natural language generation uses machine learning to mimic the ways human analysts learn from data and provide recommendations for action," says Kaushal Mody of Accenture.
"As such, the technology turns raw data into human narratives; communicating meaning in the same way people do, and providing complete transparency into how analytical decisions are made.”
NLG is similar to natural language processing. While NLP reads the text and converts it into numbers, NLG writes content.
Plus, according to the Natural Language Processing Research Report, the global market is expected to reach a whopping $22.9B in 2024. NLP combines computational linguistics (data and rule based modelling of human language) and statistical ML and deep learning models. This double act allows for the computer to process speech and words in order to extract the writer's intent.
Content Marketing Careers
Right, down to the nitty gritty. How's this all going to impact us, the hard working marketers and content writers? Well, this is only the beginning of marketing AI.
Artificial intelligence might not just automate or augment certain marketing activities, it can also alter how marketing channels work, and which skillsets are required to thrive in the near future.
This may come as part of the shift into Industry 5.0.
Industry 5.0 is a new production model which focuses on the cooperation between humans and machines. It stands for the recognition that technological advances and human insight and creativity are equally important.
But what makes it 5.0? The previous tier, industry 4.0, emerged with the arrival of automation technologies, IoT, and the smart factory. These advancements have seen the emergence of the digital industry, which have generated a new type of technology that can offer companies data-based knowledge.
Industry 5.0 comes next, involving the leveraging the collaboration between high-tech machinery and tools, and the innovation and agility of human beings.
So, the skills valued in marketers will change when AI systems are able to automatically optimise search and paid campaigns. As the technology is able to generate insightful reports, the type of analysis required of, and valued by, marketers will be different.
Plus, if AI is able to produce simple, short content, content marketers need to develop different content. Think fewer social posts, more opinion-based pieces.
So, we all know marketing skills change with the times. But with marketing AI, these skills will change faster than in the past. This doesn't mean humans will lose their advantage in the industry. Instead, they will have to identify the spaces where AI is weak, and where human creativity and agility are indispensable.
